If you would like exposure to the biggest opportunities at the intersection of VR, GenAI, Gaming and Web3 -- reply to this email to learn more about our Metaverse Ventures Fund II or schedule a call with our team.
Imagine a world in which video games are not only played, but dynamically created and shaped by AI in real-time. As a gamer and investor, I've spent months researching and discussing the possible impact of Generative AI on the gaming industry. The market map below highlights the leaders who are driving these developments, each with their own set of tools that are changing the way games are produced and enjoyed. In this article, I'll showcase some of the best demos from those startups, highlighting the latest advances in this field.
To fully understand the significance of this AI revolution in Gaming, we need to first understand the issues that the industry is suffering from. Open-world games, for example, sell unparalleled freedom and immersion yet often fall short because of repetitive dialogue, predictable behavior, and limited interactions.
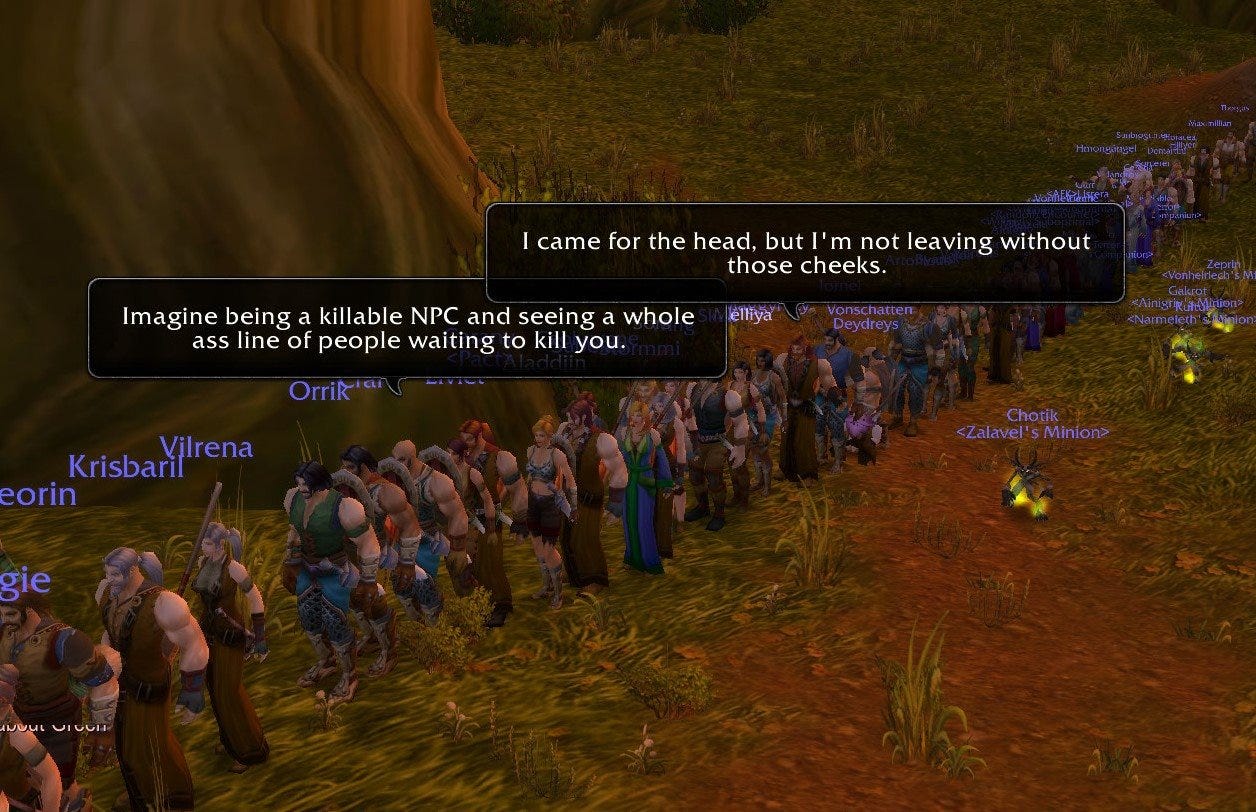
This is evident in scenes like players queuing to complete quests in World of Warcraft Classic, highlighting how traditional design struggles with large-scale player interactions.
Creating convincing NPCs and detailed environments is extremely time-consuming. Game writers create massive dialogue trees, sometimes with thousands of lines for a single character. Red Dead Redemption 2 features around 300,000 animations and 500,000 conversation lines, with even small NPCs having 80-page scripts. Even with substantial investment — Rockstar Games spent over 100,000 hours on dialogue recording — NPCs remain constrained by pre-written scripts, unable to truly react to unexpected player actions or engage in dynamic conversations. This limitation can break immersion and reveal the game world's static nature.
To address these challenges, developers have been exploring various solutions — with procedural generation as a key technique.
Procedural Content Generation uses algorithms to automatically create game content, combining human designed assets with computer randomness. This enables games like No Man's Sky or Minecraft to create nearly infinite worlds.
Another example is Tiny Glade, which started as a procedural wall generator built with the Bevy engine in Rust. It has surpassed 1 million wishlists and attracted 357,000 players for its demo, demonstrating how games offering creative tools and personalized experiences can resonate strongly with audiences, even without the scale of larger open-world titles.
Similarly, platforms like Roblox have seen remarkable growth, with daily active users surging to 79.5 million and engagement hours reaching 17.4 billion in Q2 2024.
However, procedural generation has its limits, often resulting in repetitive or predictable patterns and lack of meaningful narrative structure. Additionally, the diversity of procedurally generated content is constrained by the assets and rules the developers provide, limiting the potential for truly unique creations.
This is where generative AI emerges as a potential solution to bring this level of content richness and dynamism to traditional game formats.
The Unity Gaming Report 2024 reveals that 62% of game developers are already leveraging AI tools, with an additional 29% planning to incorporate AI into their development processes.
In May, we explored how developers are using these technologies to expand game content, with early signs of real-time creation tools starting to emerge.
NVIDIA's recent GenAI demo at SIGGRAPH 2024 showcased real-time world-building capabilities. Their NIM microservices for OpenUSD enable quick creation and assembly of 3D assets and scenes using AI and prompt engineering.
This technology points towards a future where game environments and assets are generated and adapted in real-time, with AI-driven, culturally tailored content that can be easily localized for different markets.
In March 2024, NVIDIA CEO Jensen Huang predicted at the GPU Technology Conference that fully AI-generated games could emerge within 5-10 years, potentially replacing traditional graphics rendering with AI-driven content generation.
While this vision may seem distant, Unity is already laying the groundwork with its Sentis neural inference engine. It allows developers to run AI models directly on users' devices, bypassing the need for cloud servers and ensuring faster response times and reduced latency.
This capability opens up a new realm of possibilities for creating dynamic, responsive, and personalized gaming experiences. With Sentis, game developers can implement real-time AI-driven features like adaptive gameplay, intelligent NPCs, and on-the-fly content generation. As Unity leads the way with practical tools, academic research is pushing the boundaries even further.
Runtime Behavior Generation in Games
In early August 2024, a master's research project from the University of California, Berkeley introduced GROMIT, a novel system for Runtime Behavior Generation (RBG) in video games. The project explores the use of Large Language Models (LLMs) to generate game behaviors in real-time based on player input. GROMIT demonstrates this capability through three distinct demos: a Sandbox where players can directly manipulate the environment (e.g., making an apple float or shrinking buildings), an Escape Room where object interactions are generated on-the-fly (such as burning a bookshelf with a torch), and an Adventure Game where players can combine spells to create new ones.
The research showed that GROMIT could successfully generate behaviors in 70% of cases in a controlled environment, with some generated behaviors having significant impacts on gameplay, like creating alternative solutions to puzzles. However, it also highlighted challenges, including a lower success rate (37%) in more complex, pre-existing game environments not designed for such manipulations. The study emphasizes the need for additional guardrail systems to ensure appropriate and controlled behavior generation, pointing towards a future where games could become more dynamic and personalized.
One promising example of this future direction is Determin AI's TREK platform. It is an AI Reality Engine that aims to revolutionize interactive experiences by generating millions of real-time interactive video bots.
Users will be able to watch, interact, and play with their favorite game characters and fictional worlds, as well as request new bots.
While GROMIT and TREK showcase the potential for dynamic, player-driven content generation, another crucial aspect of creating immersive, responsive game worlds lies in the behavior of non-player characters (NPCs). As games evolve to incorporate more real-time generated content, the role of NPCs in creating believable and interactive environments becomes increasingly important.
NPCs
Several companies are advancing significantly in their use of runtime generative AI to produce more interactive and dynamic characters.
Convai, for example, has shown off the possibilities of runtime produced actions by demonstrating how NPCs may react more quickly and flexibly to player interactions.
Another key player in this space is Inworld AI. Their approach centers on creating autonomous AI agents that game developers can direct and control.
Key features include the Goals and Actions system, which allows AI agents to act on developer-defined motivations triggered by player or environment interactions. These advancements make it possible to create NPCs with more depth and believable decision-making processes.
Taking NPC interaction to the next level, Ubisoft's ZeroEGGS generates stylized character gestures in real-time based on speech input. The system generalizes to new styles, voices, and languages not seen during training, creating diverse and responsive characters on-the-fly.
In user studies, it outperformed baseline models in naturalness, appropriateness, and style portrayal. This tool paves the way for more dynamic, personalized game worlds where NPC behaviors and animations adapt in real-time to player actions and preferences. Complementing these advancements in NPC behavior, innovative tools are emerging to address the challenge of dynamic asset creation.
Object Generation
Sloyd allows for on-the-fly creation of unique models based on player input or descriptions, bridging the gap between player imagination and in-game reality.
Imagine a player describing a sword with specific features to an in-game weaponsmith. Using Sloyd, the game could generate that custom weapon in real-time, bringing the player's vision to life. This technology leverages AI trained on a vast component library to interpret prompts and assemble models accordingly. This empowers developers to create more interactive and personalized game worlds, where players can shape their environment and items beyond pre-made assets.
World Building
As game developers seek to create ever more expansive and detailed environments, tools that can assist in crafting entire worlds become increasingly valuable.
Moonlander is one of the first AI-powered copilots for virtual world building, helping developers construct vast, detailed game environments with ease and speed.
Taking this concept even further, Playo.ai aims to generate fully playable, hyper-personalized 3D games at an unprecedented scale and cost-efficiency. The company is building a foundation AI model to build games on demand for people. If players want a unique game to experience (“Barbie racing in the street of Ramallah”), it will create a game in a few seconds that can be played anywhere.
The mission is to simplify game development, making it possible for anyone to transform their game ideas into reality effortlessly.
FRVR's AI-powered game creation tool, currently in public beta, enables both experienced programmers and non-coders to bring their game ideas to life. The platform streamlines the entire process from ideation to publication, allowing users to create games through simple prompts and customizable templates.
With just one click, creators can release their games on various platforms, including mobile app stores, Facebook Instant, and Microsoft Windows. Published games have been played by over 1.5 billion players globally, with some of those titles drawing in over 100 million monthly players. It demonstrates the potential for quick, AI-driven content creation. Future versions could potentially integrate into games, allowing for runtime generation of new levels, challenges, or game modes based on player preferences or actions.
Animation and Rigging
One of the most labor-intensive, costly, and skilled aspects of making a game is making great animation. Anything World has recently launched their "Animate Anything" plugin for Roblox Studio. The plugin allows users to upload their own 3D models and have them automatically rigged and animated within minutes, dramatically reducing the technical barriers to creating dynamic in-game assets.
In a similar vein, Replikant has been showcased in a presentation at SIGGRAPH 2024 as part of the Nvidia GenAI talks. The platform enables the rapid creation of high-quality 3D animations and interactive, no-code chatbots.
As we move from bringing characters and objects to life through animation, another crucial element in creating immersive game experiences is the auditory landscape.
Sounds & Music
Unlike current pre-recorded samples, AI models could produce diverse, contextually appropriate sounds on the fly. For instance, footsteps could dynamically adapt to surface types, character weight, and movement speed, creating a more realistic and varied soundscape without repetition.
ElevenLabs has recently introduced Text to Sound, which can generate a wide range of audio content, including sound effects, short instrumental tracks, soundscapes, and various character voices, all from simple text prompts.
Splash's AI music platform has gained traction, particularly through its integration with Roblox. The "Splash" game on Roblox has attracted over 21 million players, allowing them to create and perform music in-game. Splash's AI can compose, sing, rap, and play instruments, making music creation accessible to a wide audience.
This technology opens up possibilities for dynamic, personalized soundtracks in games. For runtime generated games, such technology could enable adaptive music that responds to player actions, environmental changes, or story progression, enhancing immersion without the need for extensive pre-composed soundtracks.
Ethical and Technical Considerations
One of the primary challenges facing generative AI applications across industries is the acquisition of high-quality, diverse, and ethically sourced training data. Many AI models have faced criticism for using copyrighted or personal data without proper consent, leading to legal and ethical concerns. For instance, image generation models like DALL-E and Midjourney have been scrutinized for potentially training on copyrighted artworks, while large language models have raised questions about the use of personal information scraped from the internet. Recently, NVIDIA has come under fire for allegedly scraping videos from YouTube and Netflix without permission to train its AI models, according to a report by Engadget.
In contrast to these contentious practices, Activision Blizzard has taken a notably different approach. Their recent release of the Warzone map Caldera as an open-source dataset represents a significant and proactive step in addressing AI data challenges within the gaming sector.
By openly sharing this high-quality data, Activision Blizzard is not only supporting advancements in game-related AI applications but also setting an example for ethical data sharing which also leads to more sophisticated content creation tools.
It remains to be seen whether other major gaming companies will follow suit. Nonetheless, this move demonstrates a possible path forward in balancing the need for robust AI training data with ethical considerations.
Summary
The future of gaming will likely undergo an important shift, with predictions indicating that fully AI-generated games will be available within the next five to ten years, thanks to improved GPUs that enable real-time creation of content. This approach has the potential to revolutionize various genres, from role-playing games (RPGs) to massively multiplayer online games (MMOs). One example: AI-powered non-player characters (NPCs) will engage in dynamic, unscripted interactions, greatly enhancing player immersion.
Furthermore, we believe that removing entry barriers to game production will encourage a new creator economy, enabling individuals to create high-quality games with minimal resources. This trend might give rise to 'one-person unicorns,' in which creative artists capitalize on the latest AI tools to bring their ideas to life. As a result, we also expect the average age of developers to fall dramatically, allowing in a new generation of innovation.
Disclaimers:
This is not an offering. This is not financial advice. Always do your own research. This is not a recommendation to invest in any asset or security.
Past performance is not a guarantee of future performance. Investing in digital assets is risky and you have the potential to lose all of your investment.
Our discussion may include predictions, estimates or other information that might be considered forward-looking. While these forward-looking statements represent our current judgment on what the future holds, they are subject to risks and uncertainties that could cause actual results to differ materially. You are cautioned not to place undue reliance on these forward-looking statements, which reflect our opinions only as of the date of this presentation. Please keep in mind that we are not obligating ourselves to revise or publicly release the results of any revision to these forward-looking statements in light of new information or future events.